Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the size and strength of an economy. It tells economists and investors the value of all goods and services produced in a given country or region within a certain period, giving them vital economic insights into whether their investments will be fruitful.
GDP offers data on everything from household consumption to corporate investment; it gives financiers, businesses, governments, and other financial institutions insight into how well their economies function and any potential risks they may face. Understanding GDP and its importance can help economists make more informed investment decisions.
What is GDP, and how is it measured
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a measure of the total economic output of a country in a given period, usually one year. It is calculated by adding up all the value of goods and services produced in the economy over that period.
This includes government spending, private sector businesses, investments, and exports minus imports. This figure is used to measure the performance of a nation's economy and is often compared to other countries' GDPs to assess relative economic strength.
GDP can be measured using three different methods:
- The expenditure approach, which adds up all spending on goods and services;
- The income approach, which measures total income earned by businesses, households, and governments;
- The output approach looks at the value of all goods and services produced in a given period.
GDP is an important indicator of economic health and development as it provides insight into how much money is generated and circulated within an economy. It also allows economists to compare economic growth between countries equally.
For investors, GDP is used to assess potential markets for investment and can provide useful information about the likely performance of a country’s stock market or currency.
The role of GDP in economic growth
GDP is an important indicator for economists and investors because it measures the economic activity in an economy. When GDP rises, it usually indicates that the economy is growing and people are spending more money on goods and services. On the other hand, if GDP declines, it can be a sign that the economy is slowing down and that people are spending less.
GDP can also provide insight into the economic health of a country. For example, if GDP rises faster than inflation, the economy is doing well as more money is generated and circulated. Conversely, if GDP fails to keep up with inflation, it can signal that the economy is not growing and may be heading for a recession.
GDP is an important tool for investors as it helps them assess potential investment markets. By examining GDP growth in different countries, investors can identify emerging markets with good economic prospects and make informed decisions about where to invest their money.
Finally, GDP is also used by governments to assess the effectiveness of their economic policies. By looking at changes in GDP over time, policymakers can determine whether their policies have a positive or negative impact on the economy and make adjustments as necessary.
Types of GDP

GDP can be measured in three ways: nominal, real, and per capita.
- Nominal GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced in an economy at current prices. It considers the effects of inflation or deflation on the overall economic output. This figure is often used to compare economies and assess economic growth.
- Real GDP, on the other hand, measures the total output of an economy at constant prices. This figure is used to measure economic growth over time and takes into account changes in prices due to inflation or deflation.
- Per-capita GDP measures the average output of goods and services produced per person in a given economy. This figure is used to measure the living standards of a population and compare the economic performance of different countries.
Why is GDP So Important to Economists and Investors?
GDP is an important indicator for economists and investors, providing insight into a country's economic health. It also allows them to compare economic growth between countries, assess potential investment markets, and gauge the effectiveness of government policies.
Economists and investors can make more informed decisions about allocating resources to maximize economic performance by understanding GDP. Ultimately, GDP is an essential tool for gauging the overall health of an economy and making smart investment decisions.
How the GDP affects Investors and Businesses
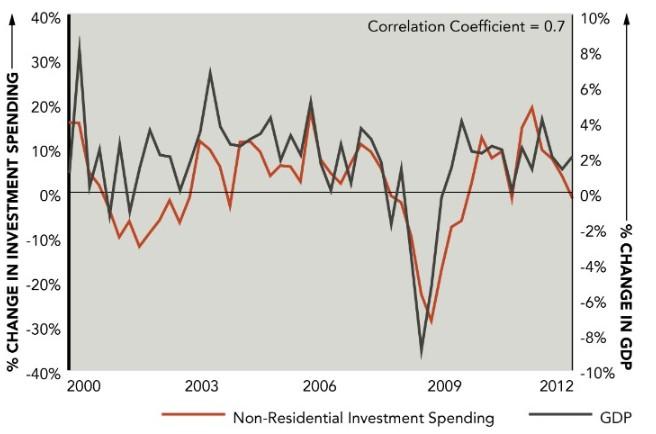
GDP is an important tool for investors and businesses as it helps them make informed decisions about investing, production, and marketing. By understanding the overall economic conditions of a country, investors can determine which markets are more likely to produce returns in the short term or the long term.
For example, if GDP is increasing, businesses may choose to expand production and marketing efforts as people are more likely to have disposable income to spend. On the other hand, if GDP is declining, businesses may scale back their production and marketing efforts so that they don’t over-invest in an economy that is not doing well.
Ultimately, GDP gives investors and businesses the information they need to make smart decisions about allocating their resources. By understanding changes in GDP over time, investors and businesses can adjust their strategies accordingly to maximize returns and minimize losses.
The pros and cons of relying on GDP as a measure of economic health
Pros of relying on GDP:
GDP provides a comprehensive view of the economic performance of a country
It allows economists and investors to compare different countries and make informed decisions about investing
It can be used as an indicator for assessing the effectiveness of government policies
Cons of relying on GDP:
GDP does not take into account external factors such as environmental factors or social inequality
It does not provide an accurate picture of the distribution of wealth within a country
GDP does not consider the quality of goods and services produced, only their quantity
FAQs
How is GDP calculated?
GDP is calculated by combining consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports. In addition to these components of GDP, changes in inventories and the foreign balance of payments are also factored into the equation.
What does a high GDP mean?
A high GDP indicates that an economy is performing well. It suggests that the economy produces a high volume of goods and services, creates jobs, and increases GDP per capita. This can be an indicator of strong economic growth.
What does a low GDP mean?
A low GDP indicates that an economy is in trouble. It suggests that the economy struggles to produce goods and services, leading to fewer jobs and lower GDP per capita. This can be an indicator of economic recession or stagnation.
Conclusion
Focusing on GDP as the exclusive measure of economic growth is easy, but it’s important to recognize when relying too much on this metric can be limiting. With that in mind, investors and businesses should consider how more nuanced economic indicators can better inform their decision-making. Ultimately, GDP is one part of a complex equation, and getting a holistic understanding of the market requires considering both traditional metrics and other forms of data.