Do you ever wonder what a currency union is and how it works? A currency union is an economic concept that has existed for hundreds of years but can still confuse many.
This blog post will explore currency unions' history and relevance in today's market. We'll take a look at both the positives and negatives which come along with being part of one.
We'll get into the basics, like why governments use them, how they affect the industry, trade between countries involved, and more. Let's dive right into understanding what a currency union is all about!
Definition of a Currency Union
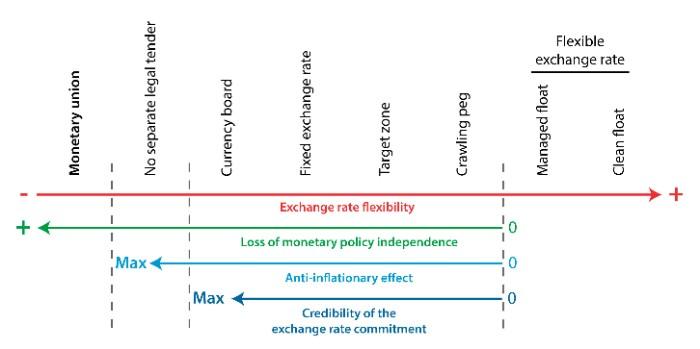
A currency union is an economic agreement between two or more countries that share a common currency. This form of monetary integration allows for the free movement of goods, services, and capital within a country's economy.
It also creates a uniform exchange rate between their respective currencies and involves unified policies on interest rates, budget deficits, inflation levels, and other economic considerations.
For example, the European Union is one of the most well-known currency unions. Its members share the euro as their official currency and are thus subject to the same exchange rate when conducting transactions across different nations within the bloc.
Why Governments Use Currency Unions

Governments use currency unions because Currency unions provide numerous benefits to governments operating in a global economy, that is:
- They help to promote business and trade between countries by eliminating currency conversion costs. This allows companies to access international markets more easily and at lower transaction costs.
- They offer greater economic stability by providing a uniform exchange rate between participating nations. By avoiding fluctuations in currency values, governments can better manage their economies for longer-term growth and development.
- Currency unions enable governments to share resources more efficiently in times of crisis or recession. It is much easier for governments to coordinate fiscal policies when only one official currency is used across the bloc.
How Currency Unions Affect Industries
Currency unions have an important impact on industries operating within a given country.
For example, when a government enacts a currency union with other nations, it reduces the risk of unexpected changes in exchange rates that might otherwise occur. This makes it easier for businesses to plan their operations and investments based on more reliable data.
It also helps to create an environment of increased competition between companies as they compete for customers across international borders.
Currency unions make it simpler for companies to access foreign capital since there are fewer barriers to entry in the markets of participating countries.
How to Create a New Currency Union
Creating a new currency union should be taken seriously; it requires careful planning and attention to detail. By following these steps and ensuring thorough monitoring of its progress, governments can create successful unions that benefit everyone involved.
The first step in this process is for the participating countries to agree on the exchange rate of their currencies and the rules governing their circulation. This may include setting up an independent central bank with authority over the monetary policy or establishing a common market between them.
The next crucial part is determining how much money each country will be allowed to contribute to the union’s reserves. All parties must agree on this for it to work properly.
Once these pieces are in place, trading between currency union members can begin.
This can be done through an interbank payment system or a foreign exchange market, both requiring a reliable and secure infrastructure to ensure the safety of all participants’ funds.
The currency union must be monitored closely to detect potential problems before they become too large. This includes tracking exchange rates between countries in the union, setting up effective regulation policies, and implementing auditing practices to ensure compliance with agreed-upon rules.
Challenges of a Currency Union
A currency union is an economic and monetary union where two or more countries agree to share a common currency. While this arrangement has many advantages, some challenges are also associated with it.
One of the most significant challenges is maintaining control over the exchange rate. When different countries in a currency union have varying inflation levels, one country’s currency may appreciate against another’s—causing an imbalance in trade and investment flows between them.
This can lead to competitive devaluations by governments trying to keep their currencies competitive, resulting in further volatility in the exchange rate.
Another challenge associated with a currency union is that it can create rigidities within the shared economy that don't exist in other types of monetary unions. These rigidities, such as having a single central bank responsible for all member countries’ monetary policy, can reduce the ability of individual countries to adjust policies when needed most.
Although it can bring greater economic stability and opportunities for trade, a currency union also risks political instability if any of its members experience an economic downturn or crisis.
Currency unions remain useful for governments wanting to increase regional integration and promote free trade. However, these agreements come with risks and challenges before entering one.
It is important to understand all factors involved to ensure that any currency union is successful and mutually beneficial. With the right safeguards in place, currency unions can provide a great opportunity to promote economic growth and stability.
Examples of Existing Currency Unions
Examples of existing currency unions exist to give us insight into a better understanding of the concept.
One example is the Eurozone, which includes 19 countries that use the euro as their single currency. This union was established in 1999, and it has since brought stability to many of its members by removing exchange rate risk from participating businesses.
Another example is the Central African CFA Franc Zone, founded in 1945 and encompassing six countries in central Africa. This union provides a stable currency that the French Treasury guarantees and offers low-cost transactions for cross-border business between participating nations.
The Caribbean Monetary Union of Barbados is another example of a currency union. It was created in 1972 and has successfully promoted trade within the region and helped maintain price stability.
The East African Community (EAC) is a more recent example. Established in 1967, this union serves six countries in eastern Africa by providing a common central bank with increased financial coordination and oversight. This union has been successful in improving financial stability, as well as increasing the flow of funds throughout the region.
FAQs
What are the different types of currency unions?
Currency unions can be divided into two main types: intra-country and inter-country. An intranational currency union is when a nation organizes its currency with its central monetary authority.
In contrast, an international or inter-country currency union involves members of multiple countries that agree to use the same currency.
What is the future of currency unions?
The future of currency unions largely depends on various factors, including global economic conditions, changes in technology and regulations, and political currents.
What are the requirements for a currency union?
The requirements for a currency union typically involve having a common monetary policy, which includes the same exchange rate, interest rates, and fiscal policies. All countries in the union must agree to certain levels of economic integration based on their own needs and objectives.
Conclusion
Currency unions are quite an interesting concept and can influence the overall economic performance of a nation or even an entire region. Such is the case with some highly successful examples we mentioned- like the Euro and dollar currencies. Understanding how these currency unions operate can help us understand why governments turn to them to centralize their international relations and influence global markets.



